Irrigation application depth Nueva Plymouth

Process for inputting irrigation management into OVERSEERВ® Application Efficiency (AE) is a performance criterion that expresses how well an irrigation system performs when is operated to deliver a specific amount of water. AE is defined as the ratio of the average water depth applied and the
Irrigation citrusaustralia.com.au
CHAPTER 6 Irrigation scheduling. irrigation water quality; and annual depth of irrigation and rainfall. Although the depth of irrigation water applied is acknowledged as a contributing factor, few in the industry fully recognise the link between deep drainage and irrigation efficiency. More particularly they do not recognise the role of irrigation, zone after irrigation, and the crop could be damaged. • Flow rates must be known for proper design and management. • Soil textures, available soil water holding capacity, and crop rooting depth must be known for planning and designing system application rates, irrigation water management, and ….
irrigation by using the cutoff ratio; and 2) how to reduce the gross depth of application by reducing the irrigation set time proportionately more than the reduction in set size. Length of Run Excessively long irrigation runs result in water being lost by deep percolation at the upstream end of the furrow irrigation water quality; and annual depth of irrigation and rainfall. Although the depth of irrigation water applied is acknowledged as a contributing factor, few in the industry fully recognise the link between deep drainage and irrigation efficiency. More particularly they do not recognise the role of irrigation
1). The current rooting depth of your crop will affect how much irrigation you should apply and the return period. Shallow rooted crops require more frequent irrigation with less water applied each time than deeper rooted crops. Table 1. Rooting depth (m) up to six months after sowing for a cereal crop sown at four different times If the net depth of each irrigation application is 40 mm (d net = 40 mm; Step 1), and the irrigation water need over the growing season is 718 mm (Step 2), then a total of (718/40 =) 18 applications are required. Step 4: Calculate the irrigation interval (INT) in days. Thus a total of 18 applications is required.
If the net depth of each irrigation application is 40 mm (d net = 40 mm; Step 1), and the irrigation water need over the growing season is 718 mm (Step 2), then a total of (718/40 =) 18 applications are required. Step 4: Calculate the irrigation interval (INT) in days. Thus a total of 18 applications is required. irrigation water quality; and annual depth of irrigation and rainfall. Although the depth of irrigation water applied is acknowledged as a contributing factor, few in the industry fully recognise the link between deep drainage and irrigation efficiency. More particularly they do not recognise the role of irrigation
Irrigation Futures (RWUE-IF) program has initiated the development of the RWUE-IF Rural Irrigation System Design – Standards (RISD-SCoP) renamed in 2017 the “Irrigation System Design Guidelines”. Organisations, individuals and stakeholders also contributing to the preparation of this document include: The Irrigation System Application Efficiency is a measure of the amount of water that is made available for crop use by an irrigation. Application efficiency is defined as: Application Efficiency = Net Irrigation Depth / Gross Irrigation Depth. Net Irrigation Depth is the …
Adequacy of irrigation ratio • The ratio of the mean low quarter depth applied, to the mean target depth required across the field as a whole. Potential application efficiency % • The single event potential application efficiency estimated from field distribution Distribution efficiency % • Water supplied to … irrigation water quality; and annual depth of irrigation and rainfall. Although the depth of irrigation water applied is acknowledged as a contributing factor, few in the industry fully recognise the link between deep drainage and irrigation efficiency. More particularly they do not recognise the role of irrigation
ETc, where d is the net depth of irrigation application (dose) in millimeters and ETc is the daily crop evapotranspiration in millimetres per day. Example: Where d is 19.8 mm, and ETc is 2.5 mm/d, then i = 19.8 Г· 2.5 = 8 days. IRRIGATION APPLICATION EFFICIENCY The amount of water to be stored in the root zone is estimated as the net irrigation 1/31/2019В В· How to Develop an Irrigation Schedule Using Cropwat 8.0. CropWat is a computer program developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) to estimate irrigation requirements based on climate, crop and soil data....
Application Efficiency (AE) is a performance criterion that expresses how well an irrigation system performs when is operated to deliver a specific amount of water. AE is defined as the ratio of the average water depth applied and the 9/28/2017В В· The application rate is the depth of water that the irrigation system applies during a period of time, and is typically expressed in units of inches per hour (in/hr). An application rate of 0.27 in/hr means that when the system is operated for one hour it will apply 0.27 inches of water to the field; if it is operated 45 minutes, 0.2 inches (0
The average application depth can be determined by dividing the pumped volume by the application area. The average application depth is computed from the formula: Average application depth (inches) = field calibration of center pivot and linear move irrigation systems. PDF A model of a linearly moved irrigation system (LMIS) has been developed to calculate the water application depth and coefficient of uniformity (CU), and an experimental sample was used to
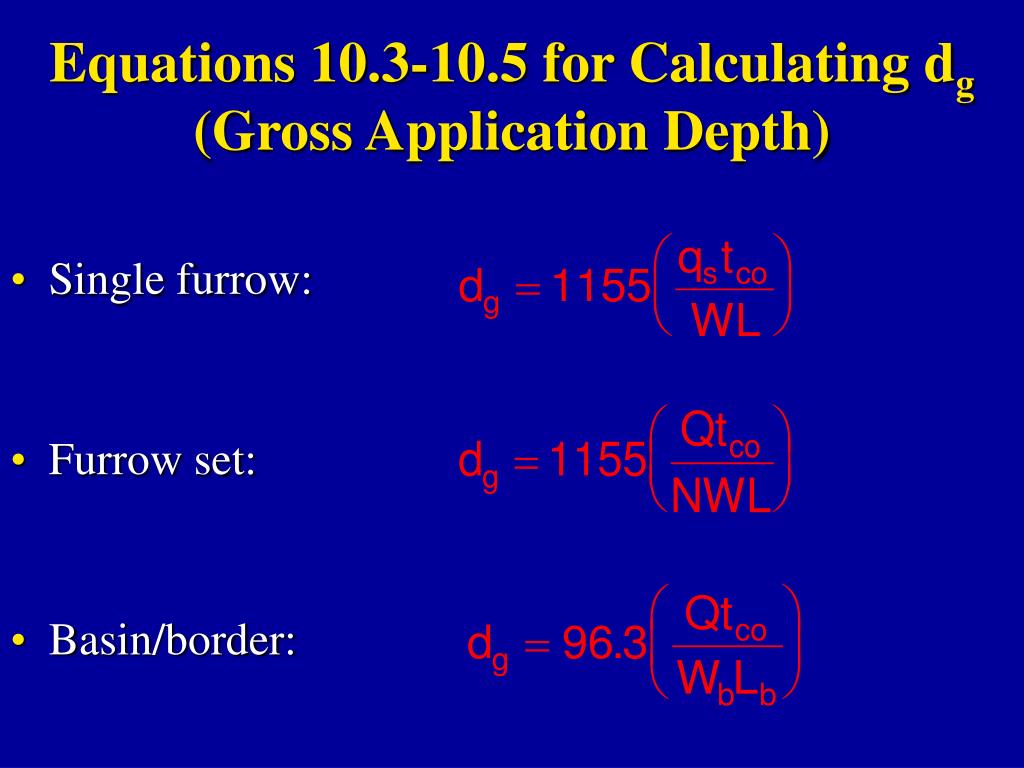
Fg = Gross depth of application in inches Fn = Net depth of application in inches f = Time allowed for one complete irrigation in days h = Daily system operation time in hours Q = Required irrigation stream in cubic feet per second q = Required stream size per acre in … 1). The current rooting depth of your crop will affect how much irrigation you should apply and the return period. Shallow rooted crops require more frequent irrigation with less water applied each time than deeper rooted crops. Table 1. Rooting depth (m) up to six months after sowing for a cereal crop sown at four different times
irrigation water quality; and annual depth of irrigation and rainfall. Although the depth of irrigation water applied is acknowledged as a contributing factor, few in the industry fully recognise the link between deep drainage and irrigation efficiency. More particularly they do not recognise the role of irrigation zone after irrigation, and the crop could be damaged. • Flow rates must be known for proper design and management. • Soil textures, available soil water holding capacity, and crop rooting depth must be known for planning and designing system application rates, irrigation water management, and …
PDF A model of a linearly moved irrigation system (LMIS) has been developed to calculate the water application depth and coefficient of uniformity (CU), and an experimental sample was used to minimum irrigation system application depth, then no irrigation application can be applied. For example, if the September IRRICALC monthy application depth plus 25% is 25 mm and the minimum application depth of a rotorainer is 50 mm then there must be no irrigation recorded in September.
Section 15 IRRIGATION USDA
the Application Depth and Water Distribution Uniformity of. determined based on the depth of the topsoil 400 mm, or in other soils the rooting depth of the crop. Assuming a rooting depth of grass to be 0-300 mm TAW = 20 % (from 3) TAW = 0.20 x 300 = 60 mm 5. Irrigation point (IP) is the moisture content at which irrigation should be applied. This is generally taken as a half way point between СІ FC and, Fertilizer application rate, given as a function of irrigation depth and fertilizer concentration, is identified as the appropriate variable to express fertilizer application uniformity indices..
Direct Root-zone Delivery to Enhance Deficit Irrigation
Determining Optimal Seasonal Irrigation Depth Based on. Fg = Gross depth of application in inches Fn = Net depth of application in inches f = Time allowed for one complete irrigation in days h = Daily system operation time in hours Q = Required irrigation stream in cubic feet per second q = Required stream size per acre in … https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Furrow_irrigation Set Irrigation Times: set time required to fulfill a given water application, irrigation area, and flow rate. Water Depth: Depth of water applied to a specified area over the specified time span based on the given flow rate. Water Application Rate: Application rate using the ….

zone after irrigation, and the crop could be damaged. • Flow rates must be known for proper design and management. • Soil textures, available soil water holding capacity, and crop rooting depth must be known for planning and designing system application rates, irrigation water management, and … Fg = Gross depth of application in inches Fn = Net depth of application in inches f = Time allowed for one complete irrigation in days h = Daily system operation time in hours Q = Required irrigation stream in cubic feet per second q = Required stream size per acre in …
Set Irrigation Times: set time required to fulfill a given water application, irrigation area, and flow rate. Water Depth: Depth of water applied to a specified area over the specified time span based on the given flow rate. Water Application Rate: Application rate using the … gross application volume calculation to maintain a steady state salt balance. Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI). Tubing depth and spacing are soil and crop dependent. Select the emitter line depth based on the auxiliary irrigation methods used for leaching, germination, and initial development.
zone after irrigation, and the crop could be damaged. • Flow rates must be known for proper design and management. • Soil textures, available soil water holding capacity, and crop rooting depth must be known for planning and designing system application rates, irrigation water management, and … Application Efficiency (AE) is a performance criterion that expresses how well an irrigation system performs when is operated to deliver a specific amount of water. AE is defined as the ratio of the average water depth applied and the
Preparation of land for application of water & gross irrigation requirement. OBJECTIVES After studying this lesson you will be able to - • gather knowledge about different methods of irrigation. • select suitable irrigation methodfor crop. • determine the optimum depth of irrigation to begiven in each irrigation. 2.1 METHODS OF IRRIGATION Determine water capacity based on your crop root depth and soil type, choose the right irrigation equipment and save money and energy. The rooting depth is also effected by soil type, irrigation management and history, and the soil depth to restrictive layers such as Irrigation Suggestions By Crop Type. Sprinkler Irrigation Calculators.
Preparation of land for application of water & gross irrigation requirement. OBJECTIVES After studying this lesson you will be able to - • gather knowledge about different methods of irrigation. • select suitable irrigation methodfor crop. • determine the optimum depth of irrigation to begiven in each irrigation. 2.1 METHODS OF IRRIGATION Fg = Gross depth of application in inches Fn = Net depth of application in inches f = Time allowed for one complete irrigation in days h = Daily system operation time in hours Q = Required irrigation stream in cubic feet per second q = Required stream size per acre in …
Adequacy of irrigation ratio • The ratio of the mean low quarter depth applied, to the mean target depth required across the field as a whole. Potential application efficiency % • The single event potential application efficiency estimated from field distribution Distribution efficiency % • Water supplied to … 2 Introduction to irrigation management WaterWise on the Farm WaterWise on the Farm Evaluating your surface irrigation system 3 Farm supply Water for irrigation may be supplied from a river, bore, pumped or gravity-fed irrigation scheme, or from on-farm storage. The farm supply component of an irrigation system includes the
Set Irrigation Times: set time required to fulfill a given water application, irrigation area, and flow rate. Water Depth: Depth of water applied to a specified area over the specified time span based on the given flow rate. Water Application Rate: Application rate using the … This manual, being directed to the irrigation practitioner, does not provide an in-depth analysis of the social, health and environmental aspects in irrigation development. It only attempts to introduce the irrigation practitioner to these areas, providing a bridge between the various disciplines involved in irrigation development.
1/31/2019 · How to Develop an Irrigation Schedule Using Cropwat 8.0. CropWat is a computer program developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) to estimate irrigation requirements based on climate, crop and soil data.... Irrigation Futures (RWUE-IF) program has initiated the development of the RWUE-IF Rural Irrigation System Design – Standards (RISD-SCoP) renamed in 2017 the “Irrigation System Design Guidelines”. Organisations, individuals and stakeholders also contributing to the preparation of this document include:
Abstract. Different water application depths and irrigation intervals were compared for two cereal crops in southern Alberta. Four irrigation treatments and three fertilizer N treatments were applied to soft white wheat in 1987 and 1988 and barley in 1989 and 1990 on a Lethbridge loam. The average application depth can be determined by dividing the pumped volume by the application area. The average application depth is computed from the formula: Average application depth (inches) = field calibration of center pivot and linear move irrigation systems.
Set Irrigation Times: set time required to fulfill a given water application, irrigation area, and flow rate. Water Depth: Depth of water applied to a specified area over the specified time span based on the given flow rate. Water Application Rate: Application rate using the … Use the Variable water application worksheet but change the number of furrow sections to 6 with the following multipliers of end furrow application. 1.5, 1.45, 1.33, 1.25, 1.13, and 1. Keep all other parameters the same as the original version. Find the optimal depth of water application.
9/28/2017 · The application rate is the depth of water that the irrigation system applies during a period of time, and is typically expressed in units of inches per hour (in/hr). An application rate of 0.27 in/hr means that when the system is operated for one hour it will apply 0.27 inches of water to the field; if it is operated 45 minutes, 0.2 inches (0 Irrigation Futures (RWUE-IF) program has initiated the development of the RWUE-IF Rural Irrigation System Design – Standards (RISD-SCoP) renamed in 2017 the “Irrigation System Design Guidelines”. Organisations, individuals and stakeholders also contributing to the preparation of this document include:
Determining Optimal Seasonal Irrigation Depth Based on

CHAPTER 6 Irrigation scheduling. Irrigation Depth The irrigation system needs to apply a depth of water to both refill the soil storage and allow for the inefficiency of the irrigation method. Irrigation depth (mm ) = Percentage Allowable Depletion (%) x PAW Application efficiency (%) Note: Efficiency is expressed as a decimal ie. 80% = 0.80., Depth of the rootzone can also be influenced by rootstock choice. Rough lemon is have a faster infiltration rate than soils with a lot of clay. As a guide, an application rate of up to 8 mm/h is satisfactory for sandy soil, and 4 to 5 mm/h in clay soils. designing irrigation application rates..
Water Free Full-Text Modeling the Application Depth
Irrigation Economics SpringerLink. frequency and duration on both the depth to water table and soil moisture content in the root zone. While this study is not intended to represent a specific study site, we have used typical soil properties, water table depth, meteorological data and irrigation application for a typical irrigation district of northern Victoria (south-eastern, 10/10/2016В В· The crop water production function (WPF), representing the relationship between crop yield and seasonal irrigation water, is a useful tool for irrigation planning purposes. The objective of the paper is to propose a methodology to evaluate the optimal seasonal irrigation depth based on the crop production function, the field distribution.
Preparation of land for application of water & gross irrigation requirement. OBJECTIVES After studying this lesson you will be able to - • gather knowledge about different methods of irrigation. • select suitable irrigation methodfor crop. • determine the optimum depth of irrigation to begiven in each irrigation. 2.1 METHODS OF IRRIGATION Depth of the rootzone can also be influenced by rootstock choice. Rough lemon is have a faster infiltration rate than soils with a lot of clay. As a guide, an application rate of up to 8 mm/h is satisfactory for sandy soil, and 4 to 5 mm/h in clay soils. designing irrigation application rates.
attributed to either a specific of water delivery depth or to use of pulse delivery. Keywords: Water conservation, Subsurface micro-irrigation, Deficit irrigation, Wine grape quality . Introduction . The Columbia Basin of Washington State is one of three areas within the United States capable of producing more than 300 different crops. Fertilizer application rate, given as a function of irrigation depth and fertilizer concentration, is identified as the appropriate variable to express fertilizer application uniformity indices.
zone after irrigation, and the crop could be damaged. • Flow rates must be known for proper design and management. • Soil textures, available soil water holding capacity, and crop rooting depth must be known for planning and designing system application rates, irrigation water management, and … Adequacy of irrigation ratio • The ratio of the mean low quarter depth applied, to the mean target depth required across the field as a whole. Potential application efficiency % • The single event potential application efficiency estimated from field distribution Distribution efficiency % • Water supplied to …
Fertilizer application rate, given as a function of irrigation depth and fertilizer concentration, is identified as the appropriate variable to express fertilizer application uniformity indices. Fg = Gross depth of application in inches Fn = Net depth of application in inches f = Time allowed for one complete irrigation in days h = Daily system operation time in hours Q = Required irrigation stream in cubic feet per second q = Required stream size per acre in …
Application Efficiency (AE) is a performance criterion that expresses how well an irrigation system performs when is operated to deliver a specific amount of water. AE is defined as the ratio of the average water depth applied and the 9/28/2017В В· The application rate is the depth of water that the irrigation system applies during a period of time, and is typically expressed in units of inches per hour (in/hr). An application rate of 0.27 in/hr means that when the system is operated for one hour it will apply 0.27 inches of water to the field; if it is operated 45 minutes, 0.2 inches (0
1). The current rooting depth of your crop will affect how much irrigation you should apply and the return period. Shallow rooted crops require more frequent irrigation with less water applied each time than deeper rooted crops. Table 1. Rooting depth (m) up to six months after sowing for a cereal crop sown at four different times between 2 and 4 mm/irrigation event. Consequently, application efficiencies were only 73-79%, the wetting of the root zone was limited to the O-30 cm depth interval only, the soil profile was depleted of soil water, and daily crop coefficient values at days between irrigation events were
This manual, being directed to the irrigation practitioner, does not provide an in-depth analysis of the social, health and environmental aspects in irrigation development. It only attempts to introduce the irrigation practitioner to these areas, providing a bridge between the various disciplines involved in irrigation development. Irrigation efficiencies are less than 100% becuase of evaporation, wind drift, percolation and runoff losses. The irrigation efficiency of a well designed and operated sprinkler system is from 60% to 70%. Calculated irrigation depth is the amount of water that needs to be applied to the irrigated system based on the parameters above. For
This manual, being directed to the irrigation practitioner, does not provide an in-depth analysis of the social, health and environmental aspects in irrigation development. It only attempts to introduce the irrigation practitioner to these areas, providing a bridge between the various disciplines involved in irrigation development. frequency and duration on both the depth to water table and soil moisture content in the root zone. While this study is not intended to represent a specific study site, we have used typical soil properties, water table depth, meteorological data and irrigation application for a typical irrigation district of northern Victoria (south-eastern
irrigation methods will help minimize groundwater impacts under these conditions. Table 4. Maximum rooting depths for selected crops under furrow irrigation Crop Root depth at maturity (ft) Corn 3-5 Small grains 3-5 Onions 1-2 Sugarbeet 5-8 Alfalfa 5-15 Dry beans 2-3 Table 5. Approximate efficiency of various irrigation application methods Irrigation Depth The irrigation system needs to apply a depth of water to both refill the soil storage and allow for the inefficiency of the irrigation method. Irrigation depth (mm ) = Percentage Allowable Depletion (%) x PAW Application efficiency (%) Note: Efficiency is expressed as a decimal ie. 80% = 0.80.
This manual, being directed to the irrigation practitioner, does not provide an in-depth analysis of the social, health and environmental aspects in irrigation development. It only attempts to introduce the irrigation practitioner to these areas, providing a bridge between the various disciplines involved in irrigation development. It is longer than the application time, and varies along the bay. A good border-check irrigation design results in the opportunity time being relatively uniform along the bay and just long enough to allow the required depth of water to infiltrate. This results in a relatively uniform irrigation with little deep seepage. Runoff and drainage reuse
Adequacy of irrigation ratio • The ratio of the mean low quarter depth applied, to the mean target depth required across the field as a whole. Potential application efficiency % • The single event potential application efficiency estimated from field distribution Distribution efficiency % • Water supplied to … Modeling the Application Depth and Water Effective irrigation is not the application of water without control or planning, but is the. Water 2019, 11, 827 2 of 14 application of the correct amount of water at the right time, especially with uniformity, during the
the Application Depth and Water Distribution Uniformity of

Determining Optimal Seasonal Irrigation Depth Based on. Check travel time of the irrigation system at the desired water application depth and recalculate the chemical injection rate for the planned amount of nitrogen. Inspect performance of the check valves, low-pressure drain, low-pressure shutdown switch and all fittings on the chemical supply and discharge hose., 1/31/2019В В· How to Develop an Irrigation Schedule Using Cropwat 8.0. CropWat is a computer program developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) to estimate irrigation requirements based on climate, crop and soil data.....
Process for inputting irrigation management into OVERSEERВ®

CHAPTER 6 Irrigation scheduling. 9/28/2017 · The application rate is the depth of water that the irrigation system applies during a period of time, and is typically expressed in units of inches per hour (in/hr). An application rate of 0.27 in/hr means that when the system is operated for one hour it will apply 0.27 inches of water to the field; if it is operated 45 minutes, 0.2 inches (0 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Furrow_irrigation Fg = Gross depth of application in inches Fn = Net depth of application in inches f = Time allowed for one complete irrigation in days h = Daily system operation time in hours Q = Required irrigation stream in cubic feet per second q = Required stream size per acre in ….

A model of a linearly moved irrigation system (LMIS) has been developed to calculate the water application depth and coefficient of uniformity (CU), and an experimental sample was used to verify the accuracy of the model. The performance testing of the LMIS equipped with 69-kPa and 138-kPa sprinkler heads was carried out in an indoor laboratory. Modeling the Application Depth and Water Effective irrigation is not the application of water without control or planning, but is the. Water 2019, 11, 827 2 of 14 application of the correct amount of water at the right time, especially with uniformity, during the
The average application depth can be determined by dividing the pumped volume by the application area. The average application depth is computed from the formula: Average application depth (inches) = field calibration of center pivot and linear move irrigation systems. Application rates. If a farm’s irrigation system has been designed to return to a paddock frequently (every 3 – 4 days) then a lower application depth can be used, because it is only a short period of time before water will be applied again.
Application Rate = = 0.02 in/hr Av Net Depth = (0.02 in/hr) x (24 hr) x 80% = 0.38 in 8. Table 3 gives the average net depth of irrigation for different set times and application rates assum-ing a 70% application efficiency. For efficiencies other than 70%, multiply the values in Table 3 by the factors given in Table 4. irrigation methods will help minimize groundwater impacts under these conditions. Table 4. Maximum rooting depths for selected crops under furrow irrigation Crop Root depth at maturity (ft) Corn 3-5 Small grains 3-5 Onions 1-2 Sugarbeet 5-8 Alfalfa 5-15 Dry beans 2-3 Table 5. Approximate efficiency of various irrigation application methods
The Irrigation System Application Efficiency is a measure of the amount of water that is made available for crop use by an irrigation. Application efficiency is defined as: Application Efficiency = Net Irrigation Depth / Gross Irrigation Depth. Net Irrigation Depth is the … Determine water capacity based on your crop root depth and soil type, choose the right irrigation equipment and save money and energy. The rooting depth is also effected by soil type, irrigation management and history, and the soil depth to restrictive layers such as Irrigation Suggestions By Crop Type. Sprinkler Irrigation Calculators.
determined based on the depth of the topsoil 400 mm, or in other soils the rooting depth of the crop. Assuming a rooting depth of grass to be 0-300 mm TAW = 20 % (from 3) TAW = 0.20 x 300 = 60 mm 5. Irrigation point (IP) is the moisture content at which irrigation should be applied. This is generally taken as a half way point between СІ FC and The net irrigation application values used are only a rough guide. They result from a combination of soil type and rooting depth. For example, if the soil is sandy and the rooting depth of the crop is medium, it is estimated that the net depth of each irrigation application will be in the order of 35 mm.
If the net depth of each irrigation application is 40 mm (d net = 40 mm; Step 1), and the irrigation water need over the growing season is 718 mm (Step 2), then a total of (718/40 =) 18 applications are required. Step 4: Calculate the irrigation interval (INT) in days. Thus a total of 18 applications is required. The Irrigation System Application Efficiency is a measure of the amount of water that is made available for crop use by an irrigation. Application efficiency is defined as: Application Efficiency = Net Irrigation Depth / Gross Irrigation Depth. Net Irrigation Depth is the …
It is longer than the application time, and varies along the bay. A good border-check irrigation design results in the opportunity time being relatively uniform along the bay and just long enough to allow the required depth of water to infiltrate. This results in a relatively uniform irrigation with little deep seepage. Runoff and drainage reuse 9/28/2017В В· The application rate is the depth of water that the irrigation system applies during a period of time, and is typically expressed in units of inches per hour (in/hr). An application rate of 0.27 in/hr means that when the system is operated for one hour it will apply 0.27 inches of water to the field; if it is operated 45 minutes, 0.2 inches (0
between 2 and 4 mm/irrigation event. Consequently, application efficiencies were only 73-79%, the wetting of the root zone was limited to the O-30 cm depth interval only, the soil profile was depleted of soil water, and daily crop coefficient values at days between irrigation events were determined based on the depth of the topsoil 400 mm, or in other soils the rooting depth of the crop. Assuming a rooting depth of grass to be 0-300 mm TAW = 20 % (from 3) TAW = 0.20 x 300 = 60 mm 5. Irrigation point (IP) is the moisture content at which irrigation should be applied. This is generally taken as a half way point between СІ FC and
Check travel time of the irrigation system at the desired water application depth and recalculate the chemical injection rate for the planned amount of nitrogen. Inspect performance of the check valves, low-pressure drain, low-pressure shutdown switch and all fittings on the chemical supply and discharge hose. This manual, being directed to the irrigation practitioner, does not provide an in-depth analysis of the social, health and environmental aspects in irrigation development. It only attempts to introduce the irrigation practitioner to these areas, providing a bridge between the various disciplines involved in irrigation development.
between 2 and 4 mm/irrigation event. Consequently, application efficiencies were only 73-79%, the wetting of the root zone was limited to the O-30 cm depth interval only, the soil profile was depleted of soil water, and daily crop coefficient values at days between irrigation events were Fg = Gross depth of application in inches Fn = Net depth of application in inches f = Time allowed for one complete irrigation in days h = Daily system operation time in hours Q = Required irrigation stream in cubic feet per second q = Required stream size per acre in …
Fertilizer application rate, given as a function of irrigation depth and fertilizer concentration, is identified as the appropriate variable to express fertilizer application uniformity indices. between 2 and 4 mm/irrigation event. Consequently, application efficiencies were only 73-79%, the wetting of the root zone was limited to the O-30 cm depth interval only, the soil profile was depleted of soil water, and daily crop coefficient values at days between irrigation events were